Pathways to the Top: How to Become a CEO
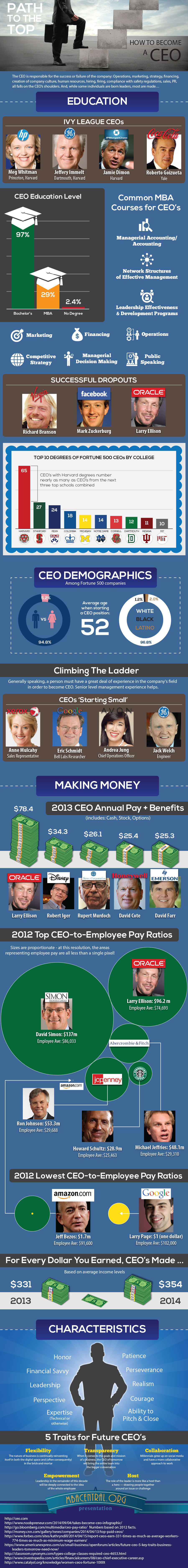
The CEO is responsible for the success or failure of the company: Operations, marketing, strategy, financing, creation of company culture, human resources, hiring, firing, compliance with safety regulations, sales, PR, all falls on the CEO’s shoulders.
Although some individuals are born leaders, most are made…
It starts with…school days:
97% of CEOs have a bachelor’s degree
29% have an MBA
2.4% have no degree at all
52: Age at which average CEO starts the job.
Want to be a CEO?
While pursuing an MBA take core courses in:
Accounting
Marketing
Financing
Operations
Managerial Decision Making,
Managerial Accounting,
Network Structures of Effective Management
Competitive Strategy
Leadership Effectiveness and Development programs
Public speaking
CEOs who are Ivy League graduates:
Meg Whitman, Hewlett-Packard, Princeton, Harvard
Jeffrey Immelt, General Electric, Dartmouth, Harvard
Jamie Dimon, J.P. Morgan Chase, Harvard
Roberto Goizueta, former CEO of Coca Cola , Yale
Drop Outs:
Richard Branson, Virgin Group
Mark Zuckerburg, Facebook
Larry Ellison, Oracle
Top 10 total degrees given to fortune 500 CEOs:
Harvard: 65
Stanford: 27
Penn: 24
Columbia: 18
Notre Dame: 14
Michigan: 14
Cornell: 13
Dartmouth: 12
Indiana: 11
MIT: 10
Is there diversity among CEOs? Not really.
[White males have a decided advantage]
Women CEOs
There are currently 24 women CEOs in the Fortune 500 and 27 in the Fortune 1000.
There are six Black CEOs of Fortune 500 companies, accounting for 1.2 percent of all Fortune 500 CEOs
There are 10 Latino CEOs of Fortune 500 companies, accounting for 2 percent of all Fortune 500 CEOs.
Working Your Way Up the Ladder
Generally speaking, a person must have a great deal of experience in the company’s field in order to become CEO. Senior level management experience helps.
How some successful CEOs started:
Anne Mulcahy, former CEO of Xerox started as a sales representative.
Eric Schmidt, former CEO of Novell and the executive chairman of Google worked in research at Bell Labs early in his career.
Andrea Jung, former CEO of Avon Products, was Chief Operation Officer at Avon before becoming CEO
Jack Welch, General Electric, started as an engineer.
Personality/characteristics of CEOs
1. Domain expertise (technology or other)
2. Leadership & personal power
3. Financial savvy
4. Ability to pitch and close
5. Honor
6. Realism
7. Perseverance
8. Patience
9. Perspective on the larger scheme of things
10. Courage to move forward, or stop, and to know when to do either one.
It’s well worth the hard work to get to the top:
Top 2013 CEO annual pay and benefits [cash, stock and options]:
1. Larry Ellison, Oracle, $78.4 million
2. Robert Iger, Disney, $34.3 million
3. Rupert Murdoch, News Corp., $26.1 million
4. David Cote, Honeywell, $25.4
5. David Farr, Emerson Electric, $25.3 million
Top 5 2012 CEO-to employee pay ratio:
1. Ronald Johnson, J.C. Penny [Note: Johnson has just been replaced]
Pay and benefits: $53.3 million
Average employee salary: $29,688
Ratio:1,795
2. Michael Jeffries, Abercrombie and Fitch
Pay and benefits: $48.1 million
Average employee salary: $29,310
Ratio: 1,640
3. David Simon, Simon Property Group
Pay and benefits: $137 million
Average employee salary: $86,033
Ratio:1,594
4. Larry Ellison, Oracle
Pay and benefits: $96,2 million
Average employee salary: $74,693
Ratio:1,287
5. Howard Schultz, Starbucks
Pay and benefits: $28.9 million
Average employee salary: $25,463
Ratio:1,135
2 Lowest CEO to employee ratios
1. Larry Page, Google
Pay and benefits: $1
Average employee salary: $102,000
Ratio:.01
2. Jeff Bezos, Amazon
Pay and benefits: $1.7 million
Average employee salary: $91,600
Ratio: 18
On average, American CEOs in 2013 earned 331 X the average worker salary: $11.3 million to $35,293.
In 2014, American CEOs earned 354 X the average worker salary.
The Future CEO: 5 key traits
1. Transparency: When it comes to the goals and mission of a business, the CEO of tomorrow will bring the entire team into the bigger conversation
2. Flexibility: The nature of business is continually reinventing itself in both the digital space and (often consequently) in the brick-and-mortar
3. Collaboration: Millennials grew up on social media and have a more collaborative approach to work
4. Empowerment: Leadership in the remainder of this decade will be deeply connected to the idea of the whole employee.
5. Host: the role of the leader is more like a host than a hero—drawing people together around an issue or challenge.
Sources:
http://www.noobpreneur.com/2014/09/04/takes-become-ceo-infographic/
http://ceo.com
http://go.bloomberg.com/multimedia/ceo-pay-ratio/ Numbers based on 2012 facts.
http://money.cnn.com/gallery/news/companies/2014/04/13/top-paid-ceos/
http://www.forbes.com/sites/kathryndill/2014/04/15/report-ceos-earn-331-times-as-much-as-average-workers-774-times-as-much-as-minimum-wage-earners/
https://www.americanexpress.com/us/small-business/openforum/articles/future-ceo-5-key-traits-business-leaders-tomorrow-need-now/
http://classroom.synonym.com/types-college-classes-required-ceo-4653.html
http://www.investopedia.com/articles/financialcareers/08/ceo-chief-executive-career.asp